LED2LEAP 2021 - Budapest Team
>>>back to working groups overview
For help with editing this Wiki page use this link.
For assignments and key readings use this link.
Landscape Democracy Rationale
- Dr. Ambedkar School is a Buddhist school with a focus on working with the Roma community. The school is located in the city of Miskolc, the city is known as an industrial town and has a very diverse townscape with many industries and housing estates, but it is mostly residential in the School surroundings. Also known as the second chance school, it is a secondary school where the students are encouraged to improve their quality of life through better education, to be able to reach the formal job market, and have a stable job with a fair wage.
- The school was moved to its location in Miskolcs in 2019 before it was located in a Roma settlement called Sájokaza to the north of Miskolc. The Roma community faces many landscape and social challenges in their settlements due to their very poor conditions. One of the main challenges is the segregation from the Roma community to the Hungarian community. Being usually placed in enclosed housing blocks or distant settlements, where the health conditions, education, and job opportunities are very poor.
- Besides keeping the students engaged, the challenges the school faces include the contrast in the landscape between the Roma settlements and the City of Miskolc, and also the school structure which is not adapted to be a school and lacks leisure areas.
Location and Scope
- Location of Dr. Ambedkar School.
The school is located in Miskolc, in the Northern region of Hungary. This is one of the poorest regions in the country, and many Roma settlements are located here. Although the city of Miskolc is the 4th biggest in Hungary, the Roma settlements around it are small, mostly ruined in structure and their residents are very poor.
Phase A: Mapping Your Community
Welcome to Your Community and Their Landscape
- The Roma community from Miskolc's surroundings and the Dr. Ambedkar School
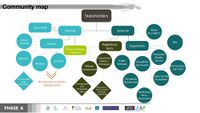
Groups of Actors and Stakeholders in Your Community
The community of Miskolc consists of two groups, social groups, and stakeholders.
I. Social groups
As we are focusing on a smaller scale, Dr. Ámbédkár school. We decided to analyze the community depending on how close they are related to the school. Those who have a close connection are the so-called inner circle. Those who have less influence or are not closely related to the school’s community are the outer circle. This is the wider community of Miskolc. One of our reasons for this division was the segregation that is happening between the inner and outer circle.
A. Inner circle
At the moment there are 100 students in the school. The students come from various places. Mostly from the surrounding poor neighborhoods, villages. Some come from Miskolc and a little percentage comes from Slovakia. The school prepares you for graduation. Their mission is to give a second chance to those who have a difficulty in graduating. There are 6 classes from 8-12. Among the students, 90% percent are from the Roma community and only 10% percent are from the Hungarian community. From the information gathered from the interviews, we heard that the future students are mostly the friends of the students. The current students tell their friends that this place is a safe place, they feel at home. Here the teachers understand, motivate and there is no discrimination between them. There is no parent association and no teacher-parent conference as well. Most of the parents cannot afford to travel to the school, they may live in other villages. Furthermore, they do not have the appropriate clothing to appear in and they live in poverty. At the moment 30 students live in the Martin Luther King Dormitory. It is a privilege to be accepted there. The students must learn more and hand in a motivation letter to apply.
B. Outer circle
Observing Miskolc’s community, we could see that there is a constant residential group. As in the kids, youth, adults, and the retired. We thought it would be relevant to focus on adults who have kids. As they can be the future students going to the school. On the other hand, there are commuters. These are the tourists who visit Miskolc, university students, seasonal workers, friends and family members of someone who lives in Miskolc, and immigrants.
II. Stakeholders
We divided the stakeholders as well into two groups. The internal and the external stakeholders.
A. Internal stakeholders
Dr. Ámbédkár school uses the teaching method called the pedagogy of love. As we mentioned above, they give a second chance to those who did not have the first one. They do everything they can within reason. Like quality education, reassurance, a nonjudgmental way of thinking, place to feel safe. These are some of the aspects of life that the students may have not experienced before. This is the reason the school calls itself the second chance school. The one that founded the school (Orsos János, director of the school) had come from the same Roma community and had to face challenges as well. The teachers and mentors are motivated, very enthusiastic in helping the students to tackle their obstacles. It is important to take account of the future employees and students as they can drastically shape the community.
B. External stakeholders
Dr. Ámbédkár school over the years had quite a few supporters. They had supported the school with learning materials, furniture, financials. They had also helped in the building of the school and the dormitory as well. The Indian Embassy is one of its greatest supporters. They organized events, festivals, leisure activities (for example, an escape room for students). Then there are the regulatory units that make rules and regulates the school structure. For example, the Educational Ministry of Hungary.
Relationships Between Your Actors and Groups
The internal social group is the most affected by the landscape challenge, especially students from the Roma community. This group has the least influence. On the other hand, you can see the clear opposite of this. Those who are not impacted by the landscape challenges are the ones to make the rules and have the most power. These are the external stakeholders. As they are involved in the school, the internal stakeholders have a high impact due to this. The school, dorm staff, and supporters have a shared interest. They want the Roma community to integrate, get adequate schooling, and for this place to be safe and comfortable. They want to demolish the cultural differences. Finally, the Miskolc community is not so impacted by challenges especially the commuters. They also have low power.
Summary of Your Learnings from the Transnational Discussion Panel
In this community, we are facing a lot of challenges first of all with a basic one: The Right to Landscape. There is a question here, what kind of a landscape is that, that this community has a right, has access to. Because of the poverty reigning in that area, there is little chance for development. So if we look at the landscape as a cultural realm two out of three points cannot be even taken into consideration here. Spiritual wellbeing is the only angle that we can approach the landscape because the Roma community has a really strong cultural heritage. If we take a look at this community of the democracy site, the situation is almost the same. Forinstance the Arnstein (1969) Ladder. In more developed countries, communities, they are a higher up. The Miskolc community is currently at the so-called „no power” stage, at the bottom, probably the manipulation is accurate. As summarised there, are so many „wicked” problems, which are very hard to solve. The main issue is that the Roma people is not being heard or represented.
Theory Reflection
The Roma community in Miskolc has a lot to develop, that is why there is no clear answer yet to what are the most important goals. The Dr. Ámbédkar School is offering youngsters the education they cannot get in a normal government school. We can translate this as a sustainable development goal, the quality education. It is still in progress but heading in the right direction. The order of the other goals is unclear. In general, the most important goals are good health and structure, reduce inequality, no poverty. In the documentary „Angry Buddha” (2016) the current principal of the school said: „In 200 years. This is not a joke. In 200 years.” That is when the situation for the gypsy people will change. As we were working during the pandemia, we faced a couple of challenges, for example, all the work was done online, we had little chance to visit the site, this way the most important thing was missing, we could not meet with the people, could not feel the place. In conclusion, the work, just as the long process, is very instructive, shocking, hard, but also funny.
References
- Ludwig, S. (Director). (2016). Angry Buddha [Documentary film].
- http://www.ambedkar.hu/
- https://www.hellomiskolc.hu/
- https://www.ksh.hu/regionalatlas_regions
- Shelley Egoz, Jala Makhzoumi and Gloria Pungetti (2011): The Right to Landscape: An Introduction
- Arnstein, Sherry R.(1969): A Ladder of Citizen Participation
Phase B: Democratic Landscape Analysis and Assessment
Tayana Passos Rosa and Angkita Hawlader's Correspondence
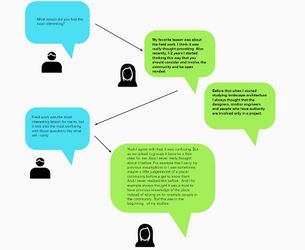
Angkita and I exchanged some emails regarding the readings. It was a pity that, because I couldn't reply during a period, I lost the opportunity to continue exchanging emails with her for this Assignment. Some communication problems occurred and I couldn't be assigned to another partner. But even though the exchange with Angkita was short, it was fruitful and I'll share here some of it and then some thoughts of my own.
Highlighting here, I'll add some of my thoughts related to the reading and our Living Lab in Budapest.
My overall reflection from the readings is that if you want to design for a community you need to first truly understand it. All knowledge is valuable, from the community experience in their everyday life, their culture, until the most specialized scientific knowledge from the professionals assigned to work in the area. And this exchange is beneficial to all because everyone learns something during this process, and every opinion weights the same. My favorite quote from all the readings is: "design with empathy rather than sympathy" (de la Pena et al. p. 10). I think this fits so well in our Budapest Living Lab situation. We are working with Dr. Ambedkar School, a Buddhist school mostly for the Roma community in Northern Hungary. The community faces a low education rate, poverty, lack of career opportunities, among many other challenges, all caused by segregation and prejudice. The school methodology tries to give the students another light on possibilities for the future through studies. I think the second chapter from de la Peña has very valuable tools to try and apply in this project, to go beyond the research of the community in a virtual environment, but also visit them in real life, experience their landscape, but especially see through their eyes and try and combine all our pieces of knowledge to achieve the best solution possible.
Linus and Max Correspondence
Nora and Patrik's Correspondence
I was quite excited and anxious as well about this type of assignment. As we have to get in touch and exchange our thoughts on literature with a complete stranger from a different country. Fortunately, I can say that from the start it was really fun and exciting. My partner was Patrik from Zagreb. First, we contacted each other via e-mail. Later on, for easier communication, we decided to use the Whatsapp platform. After exchanging the basics, we thought about what chapter should we read. Design as Democracy was for both of use the chosen literature. I read chapter 3 “Experting: They Know, We Know, and Together We Know Better, Later”. My partner read chapter 2 “Going to the People’s coming.” After reading the materials individually we shared out thoughts. Personally, I think this is a great method in engaging the students to read the readings and I have learned a lot from the book and my partner's reflections too. Later our conversation shifted to the whole Led2leap course and what lesson we liked the most. We both agreed on the so-called fieldwork lesson as it was very thought-provoking. After that, we talked about things generally. Like our studies, hobbies.
Yuga Tanaka, Kinga Fürtön and Arash Najafi Correspondence
Medya Atis and Mohadese Bagheri Correspondence
Barbara and Yasif's Correspondence
Aydin and 'Hussin Correspondence
Gabriel and 'Chloé Correspondence
- Gabriel and Chloé Correspondence.jpg
- Https://ledwiki.hfwu.de/images/d/df/Gabriel and Chloé Correspondence.jpeg
N E W
- N E W.jpg
- N E W.jpg
N E W
- N E W.jpg
- N E W.jpg
Phase C: Collaborative Visioning and Goal Setting
The Scene in Your Story of Visioning
The workshop took place at Dr. Ámbédkar School in Miskolc on May 31st. During the workshop the students selected one landscape democracy challenge out of six. They decided on: Active Schoolyard. Their idea is to make the most out of the schoolyard so more people can use it for many different things at every season of the year. The students said they want to do activities such as gardening, different types of sports, studying, reading and just chatting and relaxing with each other.
The Actors in Your Story of Visioning
Since the schoolyard is used by the students of the school they came up with several ideas for their vision with the help of the teachers, university students and kultúrAktív associates present there.
The Story of Visioning
Story-Telling 1:
How we developed goals together and how we managed to prioritize them
- Choosing Challenge
At the beginning of the workshop we started with choosing the challenge. We had 6 prepared Challenges that Anita described to them. A lot of them were also overlapping. The different challenges were laid on the floor and then the students could choose which they were most interested in on discussing or most passionate about. In the first round it was still spread and we removed the first three (two with no votes one with just one vote) and did another round and so on until it was just one challenge left. The challenge they decided for was the Active Schoolyard
- Sharing Personal Goals
In the next steps the students could write down two personal goals they had for this challenge. They briefly shared them with the group and explained them and we clustered it on the wall.
- Ranking with Votes
In the Next step we ranked the goals through votes. Every person had 5 little stickers each to put on whatever goal they found important.
- Forming Vision Groups
Then they formed Vision Groups for the best ranked 4 goals.
Story-Telling 2:
How our vision evolves
- Visioning
each groups gets a selected top goal and they prepare together a mood board on a flipchart (motto, preview pictures, drawings, visions)
Group A: “The hunger games”
Group B: “Május 6 - 6th of may - Hungarian Sports Day”
Group C: “sports field”
Group D: “school programs”
Reflect on Your Story of Visioning
- Things that needs to be considered when formulating goals:
- Characteristics of a ‚good‘ vision
- Problems
- Things that can be improved
Phase D: Collaborative Design, Transformation and Planning
Your Prototyping Action
- Dr. Ambedkar School, Miskolc
We were working with schools that are different from each other, In the condition and the age of the students, for Miskolc, the student's age started from 16 so we have to use a different way of action which motivate the students but in Budaörs we were dealing with younger children.
First and briefly I will introduce you to Miskolc, which located in the northwest east of Hungary, the school located on Main Street and the dormitory as well, the idea behind the project in Miskolc was to engage the students in the design process which aim to improve the condition of the school and its dormitory, so we went and did activities there with the students, throughout the activities students were able to interact with each other and with space and have discussions about how and what they need at this places,
- Budaörsi primary school, Budapest
In Budaörsi Primary school we created a collaborative design with 5th-grade children by using prototype and observation methods.
The Evolution of Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
The Plan Behind Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
The Realization of Your Prototyping Action
- Dr. Ambedkar school, Miskolc
First, we started with introducing ourselves to them and why we are here?
Then we started the warming-up exercise, students had to finish the sentences we already prepared while they were throwing the ball to each other. The exercise is supposed to be more fun than serious.
And then we started with where to do what exercise, moderator was saying the activities and the students decided where to do it.
Through these two exercises, we were able to select the goals and vision of the students.
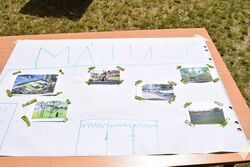
And then we moved to the main exercise which represents testing and prototypes, we give the students the opportunity to imitate the new functions in a place where they think it could happen, they could use accessories to feel it more real. While they were doing this exercise they were discussing and suggesting solutions if something seems not to work, and after we finished we come together and shared the Polaroid picture which we took during the activity and arranged the pictures into a plan on the wall and it was a space for students to leave comments, the students can later on also still comment on the pictures and all the results will be left there as an exhibition
- Budaörsi school, Budapest
First, we made students analyze their daily environment by asking them some questions. They pointed out some problems and potentials about their schoolyard. After that, they proposed some design solutions for those points and created prototypes of those design ideas. This action not only paved the way for children to interact with each other but also interact with their daily environment. As we can see from the figures all prototypes are in different scales. Students learned the term of scale and how hard it is to create an environment that they need. They understand what do they need to built or is it possible to built. They understood spatial opportunities and experienced the term of scale. Another advantage of this project is they tested their prototypes with their friends after they did it. When we look at the disadvantages as an observer I saw that materials limited them while creating their prototypes.
Reflect on Your Prototyping Action
- Comparison and reflection
Phase E: Collaborative Evaluation and Future Agendas
Collaborative Evaluation and Landscape Democracy Reflection
- insert text here
The Actors in your Collaborative Evaluation
- insert text here
Reflection on the Online Seminar
- insert text here
Reflection on the Living Lab Process
- insert text here
Your Living Lab Code of Conduct
- insert text here
Process Reflection
- insert text here