LED2LEAP 2021 - Nürtingen Team 1
>>>back to working groups overview
For help with editing this Wiki page use this link.
For assignments and key readings use this link.
| Area | blank | |
| Place | blank | |
| Country | blank | |
| Topics | blank | |
| Author(s) | blank, blank, blank, blank, blank | |

| ||
Landscape Democracy Rationale
Landscape can be seen as a product of society, which is connected to their personal history, according to Berger and Luckmann (1966). "Land", in German, can be seen as a contrast between city and countryside, including meanings such as shape, form, texture, nature, condition and manner. However, in Old High German, the landscape was associated to an object "that has the quality of a larger settlement area in most cases" (Müller, 1977). But a more recent description that fits our current location can best be described as: On's own region or nation is described in terms of its natural and cultural characteristics, so that it becomes socially available as something diametrically opposed to other regions and nations (Lekan and Zeller, 2005).
Location and Scope
- insert text here
Phase A: Mapping Your Community
Welcome to the Community and their Landscape
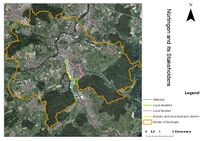
The main location is based around the river named Steinach, which is a side river from the Neckar. The Steinach river is currently not in his natural state cause of the densely built environment. So to prevent flooding grass buffers, dams and slopes are currently installed. Except for these grass buffers not much open space can be found here. Most of the parcels connecting the river are privat or used as parking space, missing the opportunity for visitors to walk along the Steinach.
Groups of Actors and Stakeholders in Your Community
- From the spatial character and land use pattern of our study area, we can see different groups of actors and stakeholders. Among the local residents, elderly citizens, kids, land owners and students are considered as important actors of our landscape. As a predominant industrial zone, we have owners, workers and local business persons. We have local clubs and municipality who are more organised actors among the groups. Another significant group we can see in the community are tourists,commuters and investors.
- Children, teenagers and retired and elderly groups are the most visible group in our landscape whereas mid-aged and working class are less visible.
- Depending on the age and social groups, the community has different needs and aspiration.Local residents want to have safety and health as well as interactive spaces.The business group and municipality have aspiration of sustainability and growth from the landscape. Tourists want to have access to attractive spaces with safety and facilities.
Relationships Between Your Actors and Groups
- insert text here
Summary of Your Learnings from the Transnational Discussion Panel
When I read about the protest privatization of a public park in Istanbul Turkey in 2013 I was shocked. I never imagined a problem like this would occur in the EU. Because enjoying and experiencing nature is a basic human right, and I never thought it would be possible to take this away from the public. However, this is not the case everywhere because after bringing this up in the discussion panel, other colleges told me they experienced the same situation.
Theory Reflection
The given theory is helpful for a critical start in this project. It gives an overview of the different meanings of the landscape. Which can have a close relationship between science and society. A very interesting statement is for example written in the "Pledge for a transformative science, written by Uwe Schneidewind, Mandy Singer-Brodowski, Karoline Augenstein and Franziska Stelze. Here is described that technological development led to an increased disconnection in society, for example, technological innovations have interfered and are still interfering with the natural and human systems. Resulting in unplanned and often until the point of no return, ecological and social side effects (Beck, 1986). That is why innovation, participation, and balance power are very important in today's society towards the landscape. Which creates the interesting discussion around Landscape democracy.
References
Schneidewind, Uwe et al (2016): Pledge for a Transformative Science - A conceptual framework Kühne, Olaf (2015): Landscape Concepts LED Team (2019):Landscape Education for Democracy
Phase B: Democratic Landscape Analysis and Assessment
The Scene in Your Story of Analysis
- insert text here
The Actors in Your Story of Analysis
- insert text here
The Story of Analysis
- insert text here
Reflect on Your Story of Analysis
- insert text here
Phase C: Collaborative Visioning and Goal Setting
The Scene in Your Story of Visioning
- insert text here
The Actors in Your Story of Visioning
- insert text here
The Story of Visioning
- insert text here
Reflect on Your Story of Visioning
- insert text here
Phase D: Collaborative Design, Transformation and Planning
Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
The Evolution of Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
The Plan Behind Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
The Realization of Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
Reflect on Your Prototyping Action
- insert text here
Phase E: Collaborative Evaluation and Future Agendas
Collaborative Evaluation and Landscape Democracy Reflection
- insert text here
The Actors in your Collaborative Evaluation
- insert text here
Reflection on the Online Seminar
- insert text here
Reflection on the Living Lab Process
- insert text here
Your Living Lab Code of Conduct
- insert text here
Process Reflection
- insert text here